In July 2024, the research paper titled “Enhancing octree-based context models for point cloud geometry compression with attention-based child node number prediction”, co-authored by the project participants – Prof. Hui Yuan, Dr Xin Lu, Mr Chang Sun, Mr Xiaolong Mao and others from De Montfort University, was accepted for publication in IEEE Signal Processing Letters. This paper focuses on the development of an attention-based child node number prediction (ACNP) module to enhance octree-based context models, with the aim of improving coding efficiency for point cloud geometry compression.
In point cloud geometry compression, most octree-based context models use the cross-entropy between the one-hot encoding of node occupancy and the probability distribution predicted by the context model as the loss. This approach converts the problem of predicting the number (a regression problem) and the position (a classification problem) of occupied child nodes into a 255-dimensional classification problem. As a result, it fails to accurately measure the difference between the one-hot encoding and the predicted probability distribution.
In this paper, we propose an attention-based module aimed at enhancing learning-based context models in octree-based geometry compression by directly predicting the number of occupied nodes.
1) We analyse why the cross-entropy loss based on one-hot encoding fails to measure the difference between the label and the probability distribution predicted by the context models.
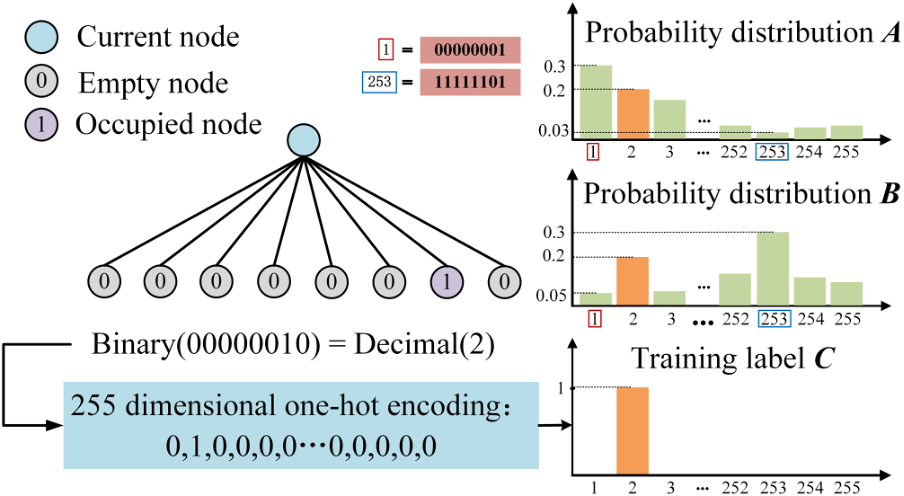
2) We introduce an attention-based child node number prediction (ACNP) module to predict the number of occupied child nodes and map it into an 8-dimensional vector containing the information about the number of occupied child nodes. The resulting 8-dimensional vector then serves as a feature to assist in training the context model.
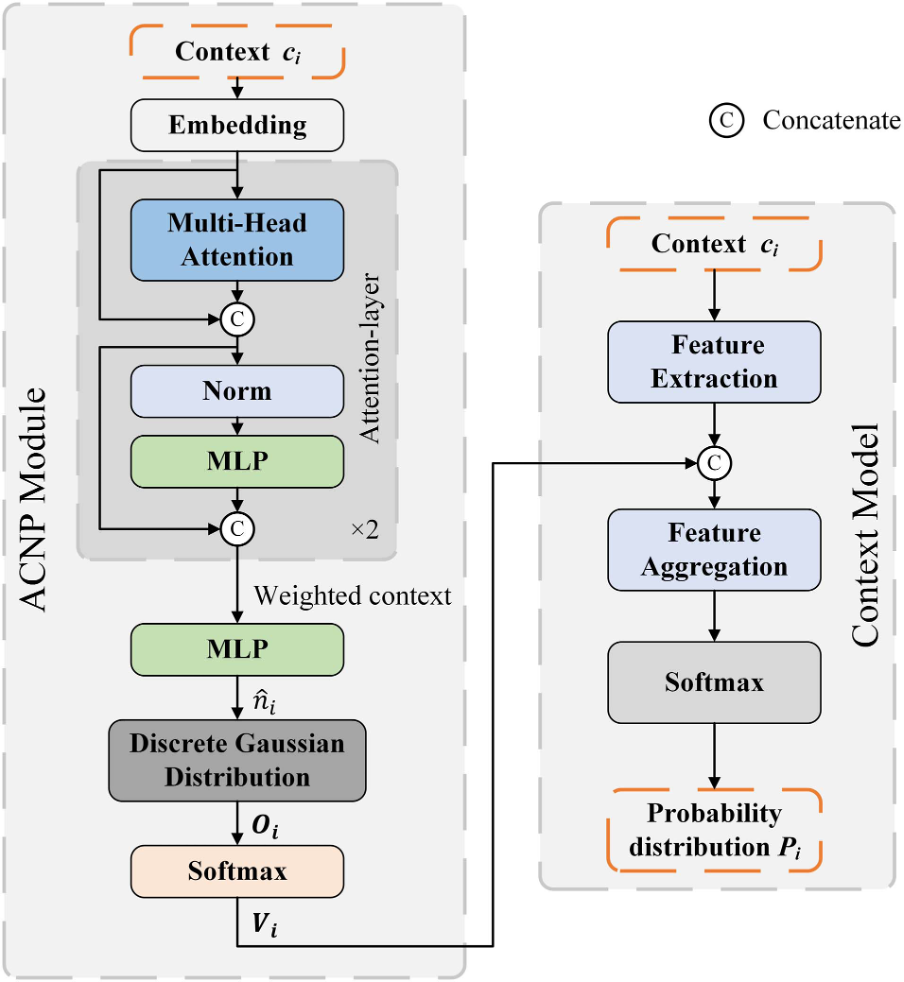
To verify the efficiency of the proposed ACNP module, we used it to enhance OctAttention [1] and OctSqueeze [2]. The resulting models are named as ACNP-OctAttention and ACNP-OctSqueeze, respectively. To validate their performance, we compared ACNP-OctAttention with OctAttention and EM-OctAttention [3], and compared ACNP-OctSqueeze with OctSqueeze. Experimental results showed that ACNP significantly improved the coding efficiency of two octree-based context models: OctAttention and OctSqueeze. However,ACNP increased the complexity of the context models.
Reference:
[1] C. Fu, G. Li, R. Song, W. Gao, and S. Liu, “OctAttention: Octree-based large-scale contexts model for point cloud compression,” in Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell., 2022, pp. 625–633.
[2] L. Huang, S. Wang, K. Wong, J. Liu, and R.Urtasun, “OctSqueeze: Octree structured entropy model for LiDAR compression,” in Proc. IEEE/CVF Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., 2020, pp. 1313–1323.
[3] C. Sun, H. Yuan, S. Li, X. Lu, and R. Hamzaoui, “Enhancing context models for point cloud geometry compression with context feature residuals and multi-loss,” IEEE Trans. Emerg. Sel. Topics Circuits Syst., vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 224–234, Jun. 2024,
